Linux Permissions Demystified: A Visual Guide to Chmod 777 vs 755
Assistools Team
Content Creator

Summary
Does 'chmod 777' make you nervous? It should. We break down the octal permission system into simple math so you never have to guess again.
I. Introduction
Understanding Linux file permissions is necessary for system administration and security management in Unix-like operating systems. You must manage who reads, writes, or executes files to maintain a secure environment. Commands like chmod define these permissions. This essay is titled Linux Permissions Demystified: A Visual Guide to Chmod 777 vs 755. It explains permissions by comparing the effects of two common settings. Graphical aids support this comparison and show the permission structure. These visuals make difficult concepts easier to understand. For instance, the layout displays how permission types apply to user categories. It highlights the difference between chmod 777 and chmod 755. This prepares the reader for a review of file security protocols.
II. Overview of Linux Permissions and Their Importance
A detailed understanding of Linux permissions helps you maintain system integrity and security. Permissions state who can read, write, or execute files. This controls access to sensitive data. The standard model sorts permissions into three classes: user (owner), group, and others. Each class has different access levels. You can show these levels in several ways. For example, a graphic representation explains the symbolic and numeric values for these permissions. It shows clearly how they work. This framework helps administrators stop unauthorized access. It limits users to files that match their roles. This strengthens system security and stability. You must understand commands like chmod. These are highlighted as necessary for file management and permission handling in Linux environments.
III. Understanding Linux File Permissions
You must understand Linux file permissions to manage systems securely. These rules decide who reads, writes, or executes files. They block unauthorized access. The chmod command lets users change these settings. It highlights the difference between modes like 777 and 755. Mode 777 grants full access to every user. This looks useful but creates major security risks. Mode 755 is safer. It restricts write permissions for the group and others. Educational materials show these differences visually. You can see examples in the visual guides provided below. These guides explain how numeric values match symbolic notations. Understanding these core rules helps users handle file security. Similar principles apply to AWS identity-based policies. This knowledge builds confidence.
IV. Explanation of Read, Write, and Execute Permissions
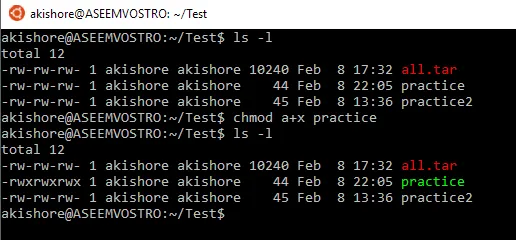
You must understand read, write, and execute permissions to manage Linux files well. Each permission type changes how users work with files and directories. The read permission (r) allows users to view file contents. Write permission (w) lets them change the file. Execute permission (x) is distinct. It lets users run programs or enter directories. You assign these permissions with symbolic notation and numbers. The command chmod 777 gives full access to everyone. But chmod 755 blocks write access for the group and others. An image helps explain these concepts. It shows the link between symbolic and numeric values. This visual aid supports the theory behind permission structures. It clarifies file security and access management.
V. The Chmod Command: Syntax and Usage
The chmod command is a central tool in Linux file permission management. It lets users set access levels for files and directories. Its distinct syntax allows for both symbolic and numeric modes. This offers options based on user preference and context. Using chmod 777 grants full permissions to the owner, group, and others. This includes read, write, and execute rights for unrestricted access. chmod 755 restricts write permission for the group and others. This restriction improves security. Yet it still allows execution and reading by all users. This access is critical for scripts and shared resources. These permissions show why users must understand the command syntax. The accompanying visual representation of permissions illustrates this point. Users can visualize the relationship between permission types and their numerical equivalents. They can then better understand the results of their choices when managing file access in Linux.
VI. Detailed Breakdown of Chmod 777 and Chmod 755
Understanding the differences between chmod 777 and chmod 755 helps manage files in Linux environments. The command chmod 777 grants full read, write, and execute permissions to the owner, group, and others. This allows anyone to modify and execute the file. But chmod 755 restricts write permissions for users other than the owner. It keeps read and execute rights for all. This distinction maintains security and allows collaborative file usage. The visual representation with this analysis explains these permission sets. It uses a color-coded model of symbolic and numeric representations to clarify their meaning. Critical files might change or disappear without the protective constraints of chmod 755. This risk shows the importance of selective permission assignment for system safety and function.

VII. Conclusion
Understanding Linux permissions is important for file security and system management. The analysis of chmod 777 versus chmod 755 shows a clear contrast between unrestricted and controlled access. This proves the need for specific permission settings based on user roles. Users prevent security risks found in loose settings. They do this by granting only necessary permissions. Visual aids depict file permissions and serve as key tools. They clarify these concepts and summarize complex ideas into simple formats. The command line examples show how to apply these permissions in real situations. They highlight the need for careful file management. This knowledge helps users decide on permission levels. It protects their systems against misuse and improves operations.
VIII. Summary of Key Differences and Best Practices for Using Chmod
You must know the difference between ‘chmod 777’ and ‘chmod 755’ to keep a Linux system secure. The first command gives read, write, and execute access to all users. This creates risks on shared systems if you use it without care. The ‘chmod 755’ command is different. It gives the owner full permissions. Group members and others receive only read and execute privileges. This option is safer. You must understand the effects on file ownership to use these commands well. Experts suggest using the strictest settings possible. This limits the chance of an attack. Visual aids show these permissions with clear pictures and numeric values. These images help users understand their choices.
References
- Boyun Zhang. "AWS Identity-based Policies with "Read", "Write" and "Execute" Actions". UWSpace (University of Waterloo), 2020,
- Sarah M. Hird, Sarah Hird. "Novel computational tools and utilization of the gut microbiota for phylogeographic inference". 2013, https://doi.org/10.31390/gradschool_dissertations.3458
More Resources
To deepen your understanding of Linux permissions, check out these authoritative external resources:
- Red Hat: Linux File Permissions Explained — A comprehensive guide by industry experts.
- ArchWiki: File Permissions and Attributes — An excellent community-maintained resource.